Anatomical reentry (anchored spiral wave)
| Optical mapping recording (left) and simulated (right) anatomical reentrant arrhythmia. The tissue has a centrally located inexcitable obstacle created by cryoablation where the propagating reentrant wave is anchored and rotates at a period of 350 ms. |
functional reentry (spiral wave)
|
|
Different types of reentrant waves can be found in cardiac tissue. Left shows a circular reentry whith a small circular core. Right shows a spiral wave with a linear core trayectory. |
Mathematical models of cardiac cells can produce many different dynamics of spiral waves. Below are shown six different spiral wave trajectories. The difference in trajectory in this case is shown as a function of tissue excitability (going from least to most).
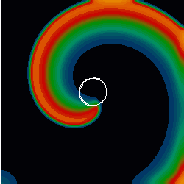 |
Circular core trajectory |
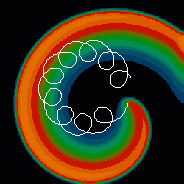 |
Epicycloidal tip trajectory |
 |
Cycloidal tip trajectory |
 |
Hypoycloidal tip trajectory |
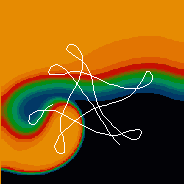 |
Hypermeander tip trajectory |
 |
Linear tip trajectory |